Answer:
A) ΔV = 1.237 V
B) K.E = 1.237 eV
Step-by-step explanation:
B)
The initial kinetic energy of the electron is given by the following formula:
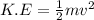
where,
K.E = Kinetic Energy of electron = ?
m = mass of elctron = 9.1 x 10⁻³¹ kg
v = speed of electron = 660000 m/s
Therefore,
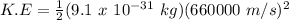
K.E = 1.98 x 10⁻¹⁹ J
K.E = (1.98 x 10⁻¹⁹ J)(
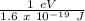 )
)
K.E = 1.237 eV
A)
The energy applied by the potential difference must be equal to the kinetic energy of the electron, in order to stop it:
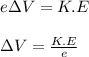
where,
e = charge on electron = 1.6 x 10⁻¹⁹ C
Therefore,
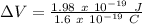
ΔV = 1.237 V