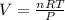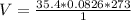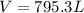Answer:
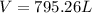
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that:
Volume
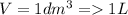
Density
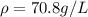
Generally the equation for Density is mathematically given by
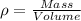
Therefore
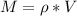
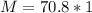
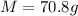
Since at STP
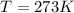
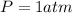
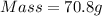
Therefore
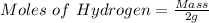
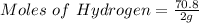
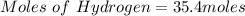
Generally the equation for Ideal gas is mathematically given by
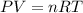
Therefore