Answer:
0.80 g
Step-by-step explanation:
First we calculate the required pOH from the given pH value:
Then we calculate the required concentration of OH⁻, using the pOH:
- [OH⁻] =
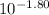 = 0.0158 M
= 0.0158 M
As the concentration of OH⁻ species is the sames as the concentration of KOH, we need to prepare 900 mL of a 0.0158 M KOH solution:
We calculate how many KOH moles are required, using the concentration and volume:
- Converting 900 mL ⇒ 900 / 1000 = 0.900 L
- moles = 0.0158 M * 0.900 L = 0.01422 mol
Finally we convert 0.01422 moles of KOH to grams, using its molar mass:
- 0.01422 mol * 56 g/mol = 0.80 g