Solution :
Given :
The sample mean = 21.3
Standard deviation = 3.2
The null hypothesis is :
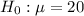
The alternate hypothesis :
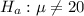
This is a two tailed test, for which a
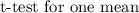 with an unknown population of a standard deviation is being used.
with an unknown population of a standard deviation is being used.
Now the significance level,
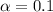 , as well as the critical value for a two tailed test is
, as well as the critical value for a two tailed test is
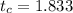
The rejection region is
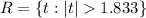
The t-statistic is computed as follows :
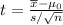
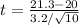
= 1.285
Since it is observed that
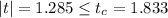 , it is then concluded that
, it is then concluded that
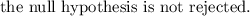
The p-value is p=0.231 and since p 0.231 ≥ 0.1, it is concluded that
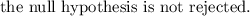
Conclusion
Thus we concluded that
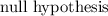
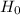 is not rejected. Therefore, the population mean
is not rejected. Therefore, the population mean
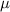 is different than 20, at the 0.1 significance level.
is different than 20, at the 0.1 significance level.