Answer:
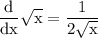
Explanation:
we want to differentiate the following by using limit:
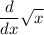
derivative definition by limit given by
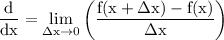
given that,
f(x)=√x
so,
f(x+∆x)=√(x+∆x)
thus substitute:
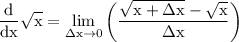
multiply both the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the numerator:
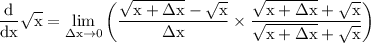
simplify which yields:
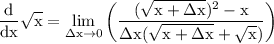
simplify square:
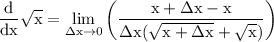
collect like terms:
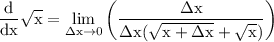
reduce fraction:
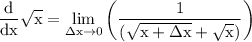
get rid of ∆x as we are approaching its to 0
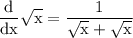
simplify addition:
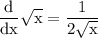
and we are done!