Answer:
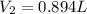
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the given information, it turns out possible for us to solve this problem by using the Boyle's law for an inversely proportional relationship between pressure and volume at constant temperature, as described in the problem statement:
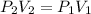
Thus, we solve for V2, final volume, to obtain the following result:
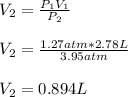
Regards!