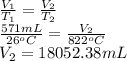Answer: The new volume at different given temperatures are as follows.
(a) 109.81 mL
(b) 768.65 mL
(c) 18052.38 mL
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
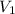 = 571 mL,
= 571 mL,
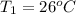
(a)
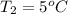
The new volume is calculated as follows.
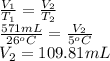
(b)
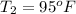
Convert degree Fahrenheit into degree Cesius as follows.
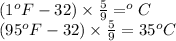
The new volume is calculated as follows.
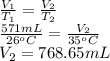
(c)
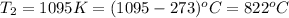
The new volume is calculated as follows.