Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
Since the pressure is constant, the only variables we need to work with are temperature and volume. We will use Charles's Law, which states the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature. The formula is:
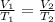
Originally, the gas was 50 milliliters at 20 degrees celsius. Substitute these values into the left side of the equation.
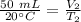
We don't know the volume of the new gas, but we know the temperature was changed to 30 degrees celsius.
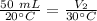
Since we are solving for the new volume, we must isolate the variable. It is being divided by 30 °Cand the inverse of division is muliplication. Multiply both sides by 30 °C.
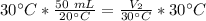
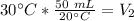
The units of degrees celsius cancel, so we are left with milliliters as the units.
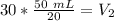
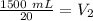
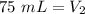
The new volume of the gas is 75 milliliters.