Answer:
d) The limit does not exist
General Formulas and Concepts:
Calculus
Limits
- Right-Side Limit:
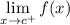
- Left-Side Limit:
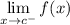
Limit Rule [Variable Direct Substitution]:
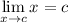
Limit Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle \lim_(x \to c) [f(x) \pm g(x)] = \lim_(x \to c) f(x) \pm \lim_(x \to c) g(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/52uan9wx0uhx7x3199mt7w68wt6nqh9a1o.png)
Explanation:
*Note:
In order for a limit to exist, the right-side and left-side limits must equal each other.
Step 1: Define
Identify
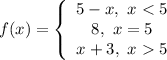
Step 2: Find Right-Side Limit
- Substitute in function [Limit]:
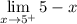
- Evaluate limit [Limit Rule - Variable Direct Substitution]:
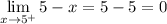
Step 3: Find Left-Side Limit
- Substitute in function [Limit]:
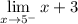
- Evaluate limit [Limit Rule - Variable Direct Substitution]:
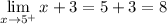
∴ Since
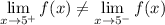 , then
, then
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Limits