Answer:
See explanation.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the description of the chemical reaction, it is possible to write the corresponding equation as follows:
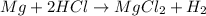
Whereas we are given the mass of magnesium and the concentration and volume of HCl; it means that we can calculate the moles of hydrogen yielded by each of these reactants in order to identify the limiting reactant:
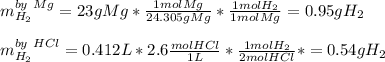
Therefore, we infer that the limiting reactant is HCl as it yields the fewest moles of hydrogen. Next since the vapor pressure of water at 81 °C is about 0.4675 atm we infer that the pressure of hydrogen is 2.23 atm - 0.4675 atm = 1.7625 atm. In such a way, we use the ideal gas equation to obtain the volume of hydrogen:

Finally, since the pressure of water is 0.4675 atm and the volume is the same for both, we obtain the moles of water and subsequently the required grams as shown below:
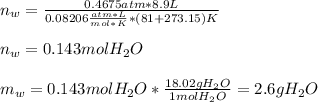
Best regards!