Answer: The ratio of the initial volume to final volume for the given gas is 27 to 127 L at constant pressure.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
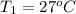
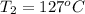
According to Charle's law, for an ideal gas pressure is directly proportional to the temperature at constant pressure.
So, formula used to calculate the ratio of the initial volume to final volume is as follows.
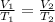
Substitute the values into above formula as follows.
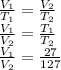
Hence, we can conclude that the ratio of the initial volume to final volume for the given gas is 27 to 127 L at constant pressure.