Answer:
r₁ = 20.5 cm
Step-by-step explanation:
In this exercise we can use the conservation of energy
the gravitational power energy is always attractive, the electrical power energy is repulsive if the charges are of the same sign
starting point.
Em₀ = U_g + U_e + K =
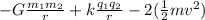
the two in the kinetic energy is because they are two particles
final point. When it is detained
Em_f = U_g + U_e =
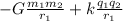
the energy is conserved
Em₀ = em_f
the charges and masses of the two particles are equal
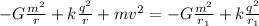
sustitute the values
-6.67-11 (4.5 10-3) ² / 0.25 - 9, 109 (30 10-9) ² / 0.25 + 4.5 10-3 4² = - 6.67 10- 11 (4.5 10-3) ² / r1 -9 109 (30 10-9) ² / r1
-5.4 10⁻¹⁵ + 3.24 10⁻⁵ - 7.2 10⁻⁵ = -1.35 10⁻¹⁵ / r₁ + 8.1 10⁻⁶ / r₁
We can see that the terms that correspond to the gravitational potential energy are much smaller than the terms of the electric power, which is why we depress them.
3.24 10⁻⁵ - 7.2 10⁻⁵ = 8.1 10⁻⁶ / r₁
-3.96 10⁻⁵ = 8.1 10⁻⁶ / r₁
r₁ = 8.1 10⁻⁶ /3.96 10⁻⁵
r₁ = 2.045 10⁻¹ m
r₁ = 20.5 cm