Answer:
9,942 bacteria were there at 10 hours.
Explanation:
Equation for population decay:
The equation for population decay, after t hours, is given by:
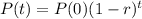
In which P(0) is the initial population and r is the decay rate, as a decimal.
Researchers recorded that a certain bacteria population declined from 200,000 to 900 in 18 hours.
This means that
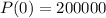 and that when
and that when
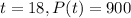 . So we use this to find r.
. So we use this to find r.
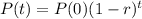
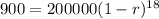
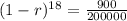
![\sqrt[18]{(1-r)^(18)} = \sqrt[18]{(900)/(200000)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/sng1cfovce5gy814sopqc81xlfnjwmsol4.png)
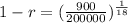
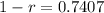
So
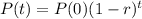
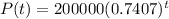
At this rate of decay, how many bacteria was there at 10 hours?
This is P(10). So
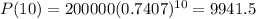
Rounding to the nearest whole number:
9,942 bacteria were there at 10 hours.