Answer:
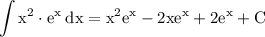
Explanation:
we want to integrate the following integration:
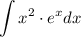
notice that, the integrand is in the multiplication of two different function in that case we can consider integration by parts given by:
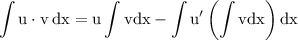
where u' can be defined by the differentiation of u
now we have to choose our u and v
which can be chosen by using the guideline:ILATE Inverse trig. , Logarithm, Algebraic expression, Trigonometry, Exponent.
since x comes first thus,
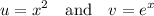
by figuring out the defferentiation of u,we acquire:
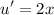
altogether we get:
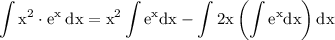
by figuring out the parentheses integration
we get:
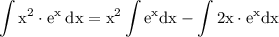
now we again have integration of two different functions so let's choose our u and v once again which can be done using the guideline
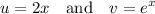
by figuring out the defferentiation of u
we acquire:
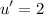
altogether we get:
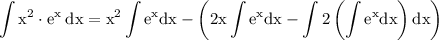
by solving parentheses we get
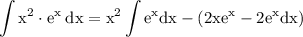
by figuring out the integral we get:
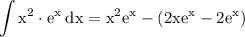
remove parentheses:
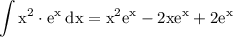
at last we of course have to add constant of integration:
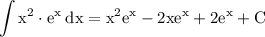
and we are done!