Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity is the moles per liter of a solution. It is found by dividing the moles of solute (glucose) by the liters of solution (water).
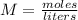
We know the molarity is 0.138 M. 1 M is equal to 1 mole per liter, so we can rewrite the molarity as 0.138 moles per liter.
There are 0.5 liters of solution.
We are solving for the moles, so we can use x.
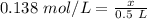
We must isolate the variable (x) to solve for the moles. It is being divided by 0.5 liters. The inverse operation of division is multiplication. Multiply both sides of the equation by 0.5 L.
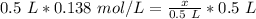
The liters on both sides cancel.
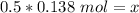
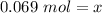
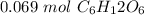
Ther are 0.069 moles of glucose in a 0.138 M solution with 0.5 liters of water.