Answer:
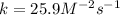
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, since rate laws are written by considering the rate constant, concentration and specific orders of reaction of the concentration of the species contributing to the rate of reaction, we write:
![r=k[A][B]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/high-school/bnuxr4iugtstgtcpofwa3c9hln8bt67qcy.png)
Since it is first-order with respect to reactant A and second-order with respect to reactant B. In such a way, given the rate and concentrations of both A and B, the involved rate constant k turns out to be:
![k=(r)/([A][B]^2) \\\\k=(2.83x10^(-5)M/s)/((0.175M)(0.00250M)^2)\\\\k=25.9M^(-2)s^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/high-school/oagfkq322ohys4ohs46z3lgyei2pah2m9w.png)
Best regards!