Answer:
23,600 collisions.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the Avogadro's law, which help us to understand the molecules-volume relationship as directly proportional:
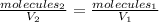
It is possible for us to compute the collisions once the volume is increased as shown below:
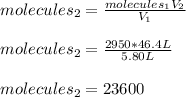
Which means 23,600 collisions will occur per square centimeter.
Regards!