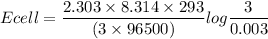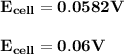Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
From the information given:
left half-cell = 3.00 mM M(NO)
right half-cell = 3.00 M M(NO)
Since the electrode are the same in both cells, then the concentration for the cell are also the same.
Negative electrode = Anode = lower concentration = 3.00 mM
Positive electrode = cathode = higher concentration = 3.00 M
Thus, right half cell will be postive electrode.
To determine the concentration cell:
![Ecell =\Big( (2.303* R* T)/(nF) \Big)log\Big(([cathode])/([anode])\Big)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/mll08rnl6jljys4p9cad5mbphd6euvg9h3.png)
SInce [Cathode] > [anode],
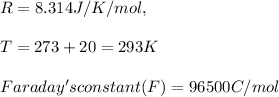
n = 3