Answer:
SAS theorem
Explanation:
Given
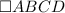
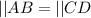
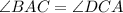
Required
Which theorem shows △ABE ≅ △CDE.
From the question, we understand that:
AC and BD intersects at E.
This implies that:
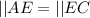
and
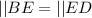
So, the congruent sides and angles of △ABE and △CDE are:
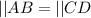 ---- S
---- S
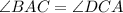 ---- A
---- A
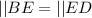 or
or
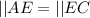 --- S
--- S
Hence, the theorem that compares both triangles is the SAS theorem