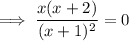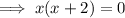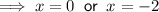Answer:
Increasing: (-∞, -2) ∪ (0, ∞)
Decreasing: (-2, -1) ∪ (-1, 0)
Constant: x = 0, x = -2
Explanation:
A function is increasing when the gradient is positive ⇒ f'(x) > 0
A function is decreasing when the gradient is negative ⇒ f'(x) < 0
A function is constant when the gradient is zero ⇒ f'(x) = 0
Given function:
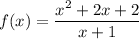
Differentiate the given function using the quotient rule.
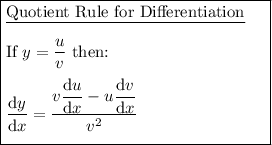
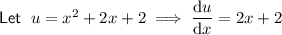
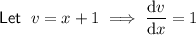
Therefore:
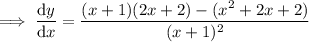
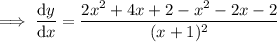
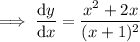
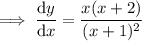
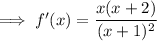
Find the critical values of the differentiated function (the zeros of the numerator and the denominator):
- Zeros of the numerator: x = 0, x = -2
- Zeros of the denominator: x = -1
Therefore, the intervals are:
- x < -2
- -2 < x < -1
- -1 < x < 0
- x > 0
Choose numbers that are within each interval and substitute them into the differentiated function:
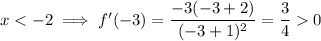
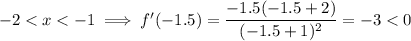
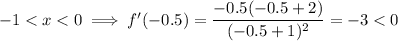
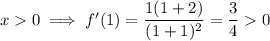
Increasing
Therefore, f'(x) > 0 when:
- x < -2 : (-∞, -2)
- x > 0 : (0, ∞)
Decreasing
Therefore, f'(x) < 0 when:
- -2 < x < -1 : (-2, -1)
- -1 < x < 0 : (-1, 0)
Constant
To find the interval where f(x) is constant, set the differentiated function to zero: