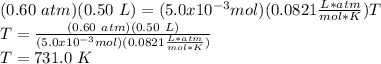Answer:
T=731.0 K
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the Ideal Gas Law, pV=nRT where
p=pressure in atm
V=volume in L
n=moles of gas
R=Ideal Gas Constant (0.08205
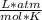 )
)
T=temperature in K
To calculate the moles of carbon dioxide, first calculate the molecular weight:
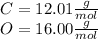
So,
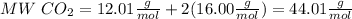
Then use the molecular weight to convert grams to moles:
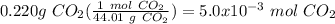
So, for this problem, let
p = 0.60 atm
V = 0.50 L
n =
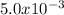 moles
moles
R = 0.0821
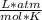
So,