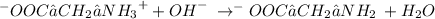Step-by-step explanation:
The chemical formula for the amino acid glycine is;
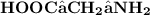
- In solution, the acidic part of the molecule that is
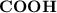 donates a proton
donates a proton
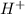 which is accepted by the basic side of the molecule which is
which is accepted by the basic side of the molecule which is
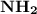 .
. - The molecule in solution becomes:
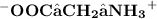
- In this state both negative and positive charges cancel out and the net charge on the molecule becomes zero.
- At a pH of 7 ( neutral state), both negative and positive charges cancel out on each each and the net charge becomes zero
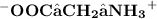
- At a pH of 12( basic state), there are more
 ions present than
ions present than
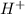 ions, the
ions, the
 ions draws a proton from
ions draws a proton from
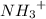 making it neutral leaving the other part of the molecule negatively charged that's
making it neutral leaving the other part of the molecule negatively charged that's
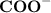 . Thus the net charge on the molecule becomes negative ( -1).
. Thus the net charge on the molecule becomes negative ( -1).