Using pythagorean theorem to find AC,
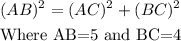
![\begin{gathered} 5^2=(AC)^2+4^2 \\ 25=(AC)^2+16 \\ (AC)^2=25-16 \\ (AC)^2=9 \\ (AC)=\sqrt[]{9} \\ (AC)=3\text{ units} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/kqh2xjticvdm219kfoyomcjc49k0iq1oph.png)
The right-angled triangles ACB and EDB,
Using the scale ratio of the sides,
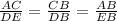
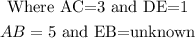
Substituting the variables,
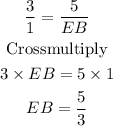
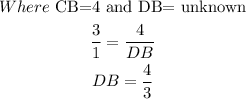
Since the ratio of the sides is AC:DE is 3:1,
Hence, the reasonable length of DE is 1 and correct option is B.