Given:
There are given that the Martina planning to fly 1000km north.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the question:
(a):
Let v represent the velocity:
So,
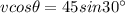
Then,
Put 500 for the value of v into the above formula:
So,
![\begin{gathered} vcos\theta=45s\imaginaryI n30^{\operatorname{\circ}} \\ 500cos\theta=45*(1)/(2) \\ cos\theta=(45)/(1000) \\ \theta=cos^(-1)(45)/(1000) \\ \theta=87.42 \end{gathered}]()
Final answer:
Hence, the direction of the pilot head is northeast because the degree of rotation is 87.42 degrees.