Given:
Time = 8.30 s ahead of the hemoglobin
For the equation of both glucose and hemoglobin:
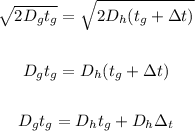
Rewrite the equation for tg:
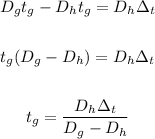
Where:
Dh is the diffusion coefficient of hemoglobin = 6.9 x 10⁻¹¹ m²/s
Dg is the diffusion coefficient of glucose = 6.7 x 10⁻¹⁰ m²/s
Δt = 8.30 seconds
Substitute these values for the variables in the equation and solve:
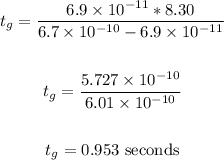
Therefore, the time that passes before the glucose is 8.30 s ahead of the hemoglobin is 0.953 seconds.
ANSWER:
0.953 seconds