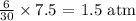Answer:
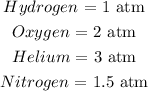
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to get the partial pressure of each gas in the container
According to Dalton's law of partial pressure, the total pressure is the sum of the partial pressures of the individual component gases
Mathematically:
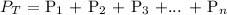
Now, to calculate for each of the gases, we divide the number of moles of the particular gas by the total number of moles and multiply by the total pressure in the container
The total number of moles will be:
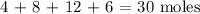
For hydrogen:
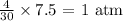
For oxygen:
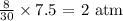
For helium:
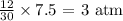
For Nitrogen: