Answer:
63/65
Explanation:
Step 1
Given that a and b are first-quadrant angles. In addition:
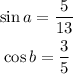
Using the double-angle formula:
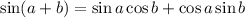
Step 2
We need to find the values of cos a and sin b.
(i)cos a
From trigonometric ratios:
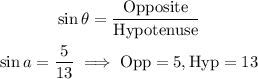
We find the length of the adjacent side using the Pythagorean Theorem.
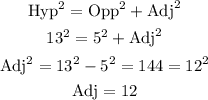
Therefore:
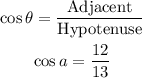
(b) sin b
From trigonometric ratios:
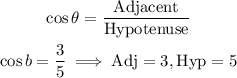
We find the length of the opposite side using the Pythagorean Theorem.
![\begin{gathered} \text{Hyp}^2=\text{Opp}^2+\text{Adj}^2 \\ 5^2=\text{Opp}^2+\text{3}^2 \\ \text{Opp}^2=5^2-3^2=25-9=16 \\ \text{Opp}=\sqrt[]{16}=4 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/buq8meeiypelz7n828e1yihgtd5iqslz06.png)
Therefore:
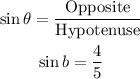
Step 3
Substitute the values of cos a and sin b into the double angle formula.
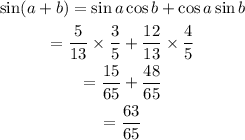
The value of sin(a+b) is 63/65.