Given data:
Mass of puck A:
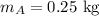
Mass of puck B:
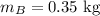
Initial velocity of puck B:
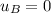
as the puck B is initally at rest.
Final velocity of puck A:
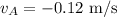
Here, negative sign indicates that the velocity of the puck A is towards left.
Final velocity of puck B:
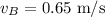
According to the conservation momentum, the momentum before and after collision remains constant that is,
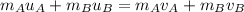
Here, uA is the velocity of puck A before collision.
Rearranging the above equation in order to get an expression uA,
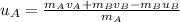
Susbtituting all known values,
![\begin{gathered} u_A=\frac{(0.25\text{ kg})*(-0.12\text{ m/s})+(0.35\text{ kg})*(0.65\text{ m/s})-(0.35\operatorname{kg})*(0)}{(0.25\text{ kg})} \\ =0.79\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}]()
Therefore, the velocity of puck A before collision is 0.79 m/s.