Given:
The equation of a function is,
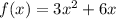
The objective is to find the point where the tangent line will be horizontal.
Step-by-step explanation:
The tangent line can be horizontal at the point where the slope value is zero.
The slope of the curve can be calculated by differentiating the equation.
To find derivative:
Let's differentiate the given function and equate to zero.
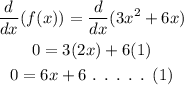
To find x :
On further solving the equation (1),
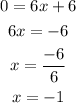
To find the (x,y):
Substitute the value of x in the given equation.
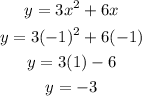
Thus, the obtained coordinate is (-1,-3).
Hence, the tangent line is horizontal at the point (x,y) = (-1,-3).