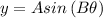
In the function above:
A is the amplitude
2π/B is the period
You equal to 0 the function and solve θ to find the points of intersection with the x-axis.
For the given function:
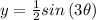
Amplitude:
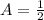
Period:
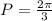
Points of intersection with the x-axis:
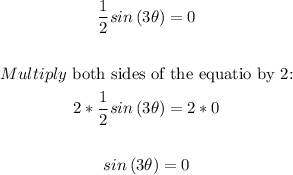
Using the unit circle you get that the angles with sine equal to 0 are: 0 and π.
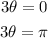
Solve θ:
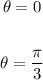
Add the period to each solution multiplied by k of θ to find all the intersections:
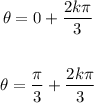
Combine the solutions:
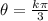
Then, the given function has Amplitude 1/2; period 2π/3, and points of intersection kπ/3 (k is a whole number)