To evaluate a function with a specific value in the domain you susbtitute in the equation of the function the independient variable (x) for the value in domain.
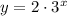
For x = -1 (a number n powered to a negative number (m) n^-m is equal to 1/n^m
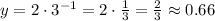
For x=0 (any number powered to 0 is equal to 1)
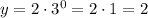
For x = 1
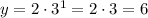
For x = 2
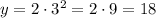
Then, as you can see as the values of the domain increase, the values of the function increase