Given,
The combined mass of the sister and the sled, m=31 kg
The angle made by the rope, θ=13°
The force applies by the student, F=290 N
The coefficient of the friction between the sled and the ground, μ=0.28
(a)
The forces that are acting on the sled in the vertical direction are upward normal force, the downward weight of the sled and the sister, and the upward vertical component of the force applied by the student.
The normal force acting on the sled is given by,
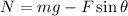
Where g is the acceleration due to gravity.
On substituting the known values,
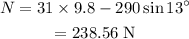
The normal force acting on the sled is 238.56 N
(b)
The net force acting on the sled in the horizontal direction is given by,
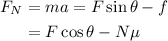
Where a is the acceleration of the sled and f is the frictional force between the sled and the ground.
On substituting the known values in the above equation,
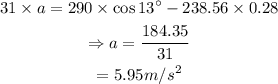
Thus the acceleration of the sled is 5.95 m/s².