Answer:
![y(x)=(x-2)^2-2\text{ }\operatorname{\Rightarrow}\text{ Opt}\imaginaryI\text{on}\operatorname{\lparen}\text{A}\operatorname{\rparen}]()
Step-by-step explanation: The provided is the graph of a parabola, therefore it can be modeled by the vertex form of the standard equation of the parabola, which is as follows:
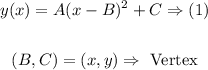
According to the graph, the vertex of the parabola is:
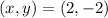
Plugging it in equation (1) results in the following:
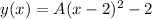
The value of the coefficient A can be determined by plugging in the coordinates of the point (4,2) in the above equation:
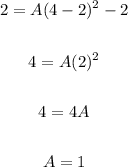
Therefore the equation that describes the graph is as follows:
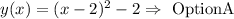
The graph confirmation: