The given problem can be exemplified in the following diagram:
To determine the velocity when the mass is located at point 2 we will consider that the change in gravitational potential energy from 1 to 2 is equal to the kinetic energy at 2, therefore, we have:
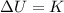
Where:
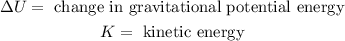
Now, we use the following formula for the gravitational potential energy:
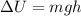
Where:
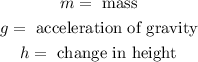
The kinetic energy is given by:
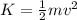
Now, we substitute the formulas:
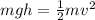
We can cancel out the mass "m":
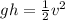
Now, we solve for the velocity by multiplying both sides by 2:
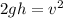
Now, we take the square root to both sides:
![\sqrt[]{2gh}=v](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/n8m0ru8dajew3fdugx4nv2gpwp8tzdtv4c.png)
Now, we determine the height "h" using the following triangle:
We notice that the adjacent side of the triangle plus the height "h" is equal to the length of the pendulum, therefore, we have the next relationship:
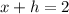
We solve for "h" by subtracting "x" from both sides:
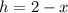
Now, we determine the value of "x" by using the function cosine:
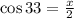
Now, we multiply both sides by 2:
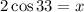
Now, we substitute the value of "x":
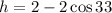
Solving the operations:
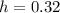
Therefore, the change in height is 0.32 meters. Substituting in the formula for the velocity we get:
![\sqrt[]{2(9.8(m)/(s^2))(0.32m)}=v](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/o5m801n8pe4pfdcacjmw4qh501vmfe6uks.png)
Solving the operations:
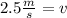
Therefore, the velocity of the mass is 2.5 m/s.