Newton's second law describes how the force applied to an object is related to a change in its motion. Therefore, the correct option is:OC.
Newton's second law of motion is a fundamental principle in classical mechanics, providing a quantitative relationship between the force acting on an object, the object's mass, and the resulting acceleration. Mathematically, the law is expressed as
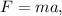 where
where
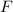 is the force applied to the object,
is the force applied to the object,
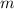 is its mass, and
is its mass, and
 is the resulting acceleration.
is the resulting acceleration.
This law emphasizes that the force exerted on an object is directly proportional to the rate of change of its momentum, or in other words, its acceleration. Furthermore, it accounts for the fact that force and acceleration are both vector quantities, with the direction of the force influencing the direction of the acceleration.
Newton's second law refutes the notion that objects at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by an external force (as suggested by Newton's first law). Instead, it asserts that the application of force leads to changes in an object's motion, quantifying this relationship. This law is integral in understanding and predicting the motion of objects under the influence of forces, forming a cornerstone in classical mechanics and laying the foundation for the study of dynamics and kinematics.