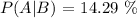This problem is about conditional probability, where:
P(A | B) = Probability of A given B
P(A ∩ B) = Probability of A and B
P(B) = Probability of B
And the relation with the terms above is:
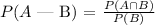
In order to calculate de probabilities we need to sum over the students:
Total number of students = 100 (we just sum all the numbers in the table)
Now, the events are:
A = take the bus
B = be a senior student
P(A ∩ B) = # of senior students that take the bus / total number of students = 5 / 100 = 0.05
P(B) = # of senior students / total number of students = 35 / 100 = 0.35
So, using the formula of above:
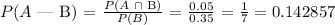
Or: