Since we know that for x = 6 we'll have a zero, we can perform a division by
(x -6).
First, we write down our problem in the synthetic division format:
After this, we write down the first coefficient without changes:
Now, we multiply the entry in the left part of the table by the last entry in the result row (under the horizontal line).
After this, we add the obtained result to the next coefficient of the dividend, and write down the sum.
We repeat this step for the following coefficients:
After following these steps, we would have completed the division. We got as a result 1, -4, 5, 0 . All the coefficients, except for the last one, are the coefficients of the quotient, the last coefficient is the remainder.
Thus the quotient is:
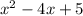
And the remainder is 0.
Using this result we can factor our original polynomial:
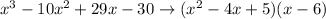
Since our first factor cannot be factored any further, we conclude that the only real-valued zero of the function comes from (x - 6)
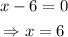
Therefore, we can conclude that the only zero of our function is x = 6