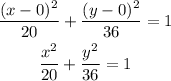Since the x-coordinates are equal, the ellipse is vertical. Thus, the standard equation of the ellipse is as follows:
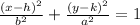
Since the x-coordinates of the foci and the vertex are the same, the value of h must be 0.
Equate the y-coordinates of the foci to the following.
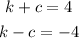
Add the two equations and then solve for k.
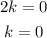
Thus, the center is at (0,0) or the origin.
To solve for c, substitute the value of k into k+c=4.
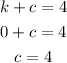
To solve for a, equate the y-coordinate of the vertex to k+a.
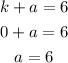
Solve for a².
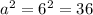
To solve for b², substitute the value of a and c into the following equation.
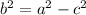
Thus, we obtain the following:
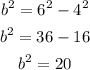
Substitute the values into the equation of the ellipse. Thus, we obtain the following: