The polynomial is given below as

Step 1:The polynomial can be factorized by using the rational root test. To apply this test first we need to find at least one rational zero.
From the root test, we can deduce that
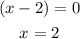
Check:
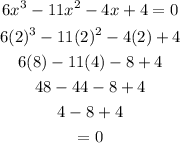
Is a factor of the polynomial above
Step 2:Divide

By

Using the synthetic division, we will have the quotient of the division be
From the steps above, we can see that
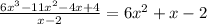
That is,
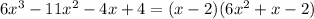
Step 3: Factorize the quadratic expression below
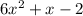
To do this, we will have to look for two factors that will give a product of (6^-2 =-12) and the same two factors that will give a sum of +1
Using the try and error method, the two factors are
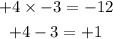
Replace +x with the +4x-3x below as
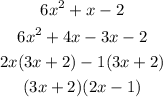
Hence,
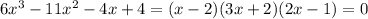
To find the zeros, we will equate each factor to be =0
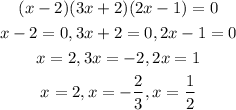
Therefore,
The final values for x are
x=2
x= -2/3
x=1/2