The question requires us to calculate the amount of heat energy necessary to change the temperature of a given mass of iron from −2.6°C to 14.9°C.
The following information was provided by the question:
mass of iron: 790.0g
initial temperature: −2.6°C
final temperature: 14.9°C
heat capacity of iron: 0.449J/gK
To calculate the amount of heat necessary, we can use the following equation:
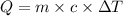
where Q is the amount of heat (in J), m is the mass of the sample (in g), c is the specific heat capacity (given in J/g.K) and ΔT is the variation of temperature (in K). (Note that the units used are defined by the unit of the specific heat capacity)
To calculate the amount of heat, we need to know the variation of temperature in the process.
As the initial temperature was -2.6°C (270.55 K) and the final temperature, 14.9°C (288.05 K), the total variation was 17.5°C (or 17.5 K) - the temperature needs to achieve 0°C (+2.6°C) and then increase more 14.9°C (2.6+14.9).
Now, we can calculate the heat energy:
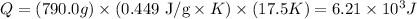
Therefore, the amount of heat energy necessary to heat a mass of 790.0g of iron from -2.6°C to 14.9°C is 6.21 x 10^3 J (or 6.21 kJ).