Solution
- The function given is:
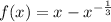
- Rolle's theorem states that:
"if a function f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] and differentiable on the open interval (a, b) such that f(a) = f(b), then f′(x) = 0 for some x with a ≤ x ≤ b."
- The Rolle's theorem formula is:
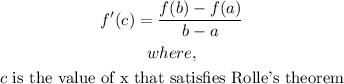
- The interval given to us is [0, 1], this implies that:
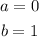
- We can confirm that:
![\begin{gathered} f(a)=f(0)=0-0^{-(1)/(3)}=0-\frac{1}{0^{(1)/(3)}} \\ f(a)=undefined \\ f(b)=f(1)=1-1^{-(1)/(3)}=0 \\ \\ \therefore f(a)\\e f(b) \end{gathered}]()
- Thus, since the values of f(a) and f(b) are not equal, no value of c would satisfy the Rolle's theorem