Given:
A(1,2)
B(3,4)
C(3,-1)
D(1,-3)
Solution:
We are asked to justify the argument using the slope formula and the distance formula.
Slope Formula:
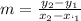
Distance Formula:
![d=\sqrt[]{(x_2_{}-x_1)^2^{}_{}+(y_2-y_1_{})^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/be9w9rxfojr83l2b0nehxx3n6f2jv0jtt7.png)
Now, we will use the given to find the slope and the distance inorder to answer the questions.
For the slopes:
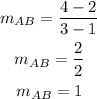
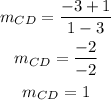
The slopes of AB and CD are equal.
For the distances:
![\begin{gathered} d_(AB)=\sqrt[]{(3_{}-1_{})^2_{}+(4_{}-2_{})^2} \\ d_(AB)=\sqrt[]{2^2+2^2} \\ d_(AB)=\sqrt[]{8} \\ d_(AB)=2\sqrt[]{2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/m0ru2dag1h99abgamdw6ymvaz3tah4u657.png)
![\begin{gathered} d_(CD)=\sqrt[]{(1_{}-3_{})^2_{}+(-3_{}+1_{})^2} \\ d_(CD)=\sqrt[]{(-2)^2+(-2)^2} \\ d_(CD)=\sqrt[]{8} \\ d_(CD)=2\sqrt[]{2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/gxmbfzidjzn18wsz7h6aawboapqbqth9bz.png)
ANSWER:
Yes, ABCD is a paralellogram.
AB is equal to CD and the slopes of AB and CD are equal, so one pair of opposite sides is both parallel and congruent.