a. This can be gotten from the equation of reaction. An easy way about this is always consider the reactant dissipating and carries a negative sign while the foward reaction carries the postive sign since products is formed.
The differential rate of the reaction can be written as
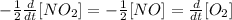
b.
But the rate ofthe reaction is
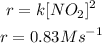
Now, let's bring the differential equation back
![undefined]()