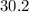Recall the following formula for motion at constant acceleration:
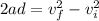
Where a represents the acceleration, and d represents the distance traveled while accelerating from the initial velocity v_i to the final velocity v_f.
First, solve for the distance d:
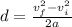
The values of v_f and v_i are known, and the value of a can be calculated using the definition of acceleration:
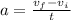
Substitute v_f=4.4 m/s, v_i=1.9 m/s and t=9.6s to find the acceleration:
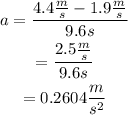
Next, substitute a=0.2604 m/s^2 as well as v_f=4.4 m/s and v_i=1.9 m/s into the formula for d to find the traveled distance:
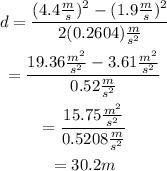
Therefore, the traveled distance in meters is equal to: