Solution:
Given the parallelogram below:
According to the properties of a parallelogram, the opposite sides are parallel and equal in dimensions.
Thus,
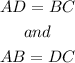
A) Height of the parallelogram:
The length BE is the height of the parallelogram, which is evaluated using the Pythagorean theorem.
According to the Pythagorean theorem,
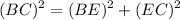
Where
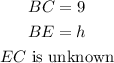
To evaluate h, we need to determine the value of EC.
Recall that
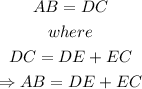
Thus, we have
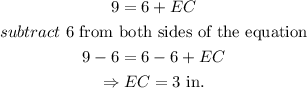
We can now determine the value of h.
From the Pythagorean theorem,
![undefined]()