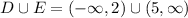A real number is a value of a continuous quantity that can represent a distance along a line. It includes all numbers, except complex numbers.
The set D is defined as all numbers less than 2, while the set E represents all the numbers greater than 5.
D ∩ E: This means the intersection of sets D and E. The intersection of two sets is the set of the elements that are in both sets.
Since D contains all numbers less than 2 and E contains all the numbers greater than 5, the intersection contains no elements, since no elements from D exist in E.
Hence,
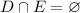
D ∪ E: This means the union of sets D and E. The union of two sets contains all the elements contained in either set (or both sets).
The union of D and E includes all real numbers less than 2 (from set D) and all numbers greater than 5 (from set E).
In interval notation, it is given as: