Answers:
(a) a = -90 m/s² or 9.18g
(b) t = 0.00667 s
(c) a = -40 m/s² or 4.08g
Step-by-step explanation:
When the acceleration is constant, we can use the following equation:
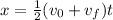
Where x is the distance, v0 is the initial velocity, vf is the final velocity and t is the time. So, replacing x by 2 mm (0.002 m), v0 by 0.6 m/s, and vf by 0 m/s, we can solve for t as:
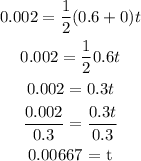
Therefore, the stopping time is 0.00667 s.
With this time we can calculate the acceleration using the following equation:
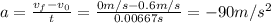
Then, to know the acceleration as a multiple of g, we need to divide 90 m/s² by 9.8 m/s² to get:
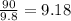
So, 90 m/s² is equivalent to 9.18g
In the same way, we can calculate the acceleration when the distance is 4.5 mm (0.0045 m). So, the stopping time is equal to:
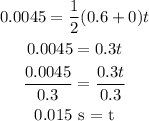
Then, the acceleration is equal to:
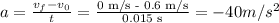
Since 40/9.8 = 4.08g, we can say that -40m/s² is equivalent to 4.08g.