We are given that a boat travels upstream a distance of 275 kilometers in 5 hours. This is the speed of the boat when it goes against the current of the river, therefore, we have:
![v_b-v_r=\frac{275\operatorname{km}}{5h}]()
Where:
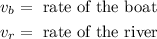
Simplifying we get:
![v_b-v_r=55\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}]()
Now, when the boat travels downstream then the relative speed of the boat is determined by adding both velocities, therefore, we have:
![v_b+v_r=\frac{372\operatorname{km}}{4h}]()
Simplifying we get:
![v_b+v_r=93\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}]()
Now we have two equations and two variables. To solve the system we can add both equations and we get:
![v_b-v_r+v_b+v_r=93\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}+55\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}]()
Adding like terms:
![2v_b=148\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}]()
Now we divide both sides by 2:
![v_b=\frac{148\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}}{2}=74\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}]()
Therefore, the rate of the boat is 74 km/h. To determine the rate of the river we substitute this rate in the first equation:
![74\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}_{}-v_r=55\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}]()
Now we solve for the rate of the rive first by subtracting 74 from both sides:
![-v_r=55\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}-74\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}]()
Solving the operations:
![-v_r=-19\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}]()
Now we multiply both sides by -1:
![v_r=19\frac{\operatorname{km}}{h}]()
Therefore, the rate of the river is 19 km/h.