Answer
The moles of O2 in the sample = 4.71 mol
Step-by-step explanation
Given:
Temperature, T = 294 K
Pressure, P = 3.55 atm
Volume, V = 32.0 L
The ideal gas constant, R = 0.0821 L*atm/mol*K
What to find:
The number of moles, n of O2 in the sample.
Solution:
The number of moles, n of O2 in the sample can be calculated using the ideal gas equation.
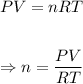
Plugging the values of the parameters into the formula, we have;
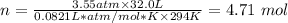
The number of moles, n of O2 in the sample = 4.71 mol