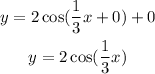The general equation of cosine function is:
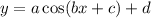
where:
a = amplitude
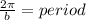
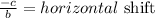
d = vertical shift
In this case, we have no vertical nor horizontal shifts, then:
c = 0
d = 0
The amplitude is 2, then:
a = 2
The period is 6π, then:
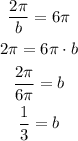
Substituting this information into the general equation, we get: